ISBI 2012 Simple 2D Multicut Pipeline¶
Here we segment neuro data as in [BPR+17]. In fact, this is a simplified version of [BPR+17]. We start from an distance transform watershed over-segmentation. We compute a RAG and features for all edges. Next, we learn the edge probabilities with a random forest classifier. The predicted edge probabilities are fed into multicut objective. This is optimized with an ILP solver (if available). This results into a ok-ish learned segmentation for the ISBI 2012 dataset.
This example will download a about 400 MB large zip file with the dataset and precomputed results from [BPR+17]
# multi purpose
import numpy
import scipy
# plotting
import pylab
# to download data and unzip it
import os
import urllib.request
import zipfile
# to read the tiff files
import skimage.io
import skimage.filters
import skimage.morphology
# classifier
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
# needed parts of nifty
import nifty
import nifty.segmentation
import nifty.filters
import nifty.graph.rag
import nifty.ground_truth
import nifty.graph.opt.multicut
Download ISBI 2012:¶
Download the ISBI 2012 dataset and precomputed results form [BPR+17] and extract it in-place.
fname = "data.zip"
url = "http://files.ilastik.org/multicut/NaturePaperDataUpl.zip"
if not os.path.isfile(fname):
urllib.request.urlretrieve(url, fname)
zip = zipfile.ZipFile(fname)
zip.extractall()
Setup Datasets:¶
load ISBI 2012 raw and probabilities for train and test set and the ground-truth for the train set
rawDsets = {
'train' : skimage.io.imread('NaturePaperDataUpl/ISBI2012/raw_train.tif'),
'test' : skimage.io.imread('NaturePaperDataUpl/ISBI2012/raw_test.tif'),
}
# read pmaps and convert to 01 pmaps
pmapDsets = {
'train' : skimage.io.imread('NaturePaperDataUpl/ISBI2012/probabilities_train.tif'),
'test' : skimage.io.imread('NaturePaperDataUpl/ISBI2012/probabilities_test.tif'),
}
pmapDsets = {
'train' : pmapDsets['train'].astype('float32')/255.0,
'test' : pmapDsets['test'].astype('float32')/255.0
}
gtDsets = {
'train' : skimage.io.imread('NaturePaperDataUpl/ISBI2012/groundtruth.tif'),
'test' : None
}
computedData = {
'train' : [{} for z in range(rawDsets['train'].shape[0])],
'test' : [{} for z in range(rawDsets['test'].shape[0])]
}
Helper Functions:¶
Function to compute features for a RAG (used later)
def computeFeatures(raw, pmap, rag):
uv = rag.uvIds()
nrag = nifty.graph.rag
# list of all edge features we fill
feats = []
# helper function to convert
# node features to edge features
def nodeToEdgeFeat(nodeFeatures):
uF = nodeFeatures[uv[:,0], :]
vF = nodeFeatures[uv[:,1], :]
feats = [ numpy.abs(uF-vF), uF + vF, uF * vF,
numpy.minimum(uF,vF), numpy.maximum(uF,vF)]
return numpy.concatenate(feats, axis=1)
# accumulate features from raw data
fRawEdge, fRawNode = nrag.accumulateStandartFeatures(rag=rag, data=raw,
minVal=0.0, maxVal=255.0, numberOfThreads=1)
feats.append(fRawEdge)
feats.append(nodeToEdgeFeat(fRawNode))
# accumulate data from pmap
fPmapEdge, fPmapNode = nrag.accumulateStandartFeatures(rag=rag, data=pmap,
minVal=0.0, maxVal=1.0, numberOfThreads=1)
feats.append(fPmapEdge)
feats.append(nodeToEdgeFeat(fPmapNode))
# accumulate node and edge features from
# superpixels geometry
fGeoEdge = nrag.accumulateGeometricEdgeFeatures(rag=rag, numberOfThreads=1)
feats.append(fGeoEdge)
fGeoNode = nrag.accumulateGeometricNodeFeatures(rag=rag, numberOfThreads=1)
feats.append(nodeToEdgeFeat(fGeoNode))
return numpy.concatenate(feats, axis=1)
Over-segmentation, RAG & Extract Features:¶
- Compute:
- Over-segmentation with distance transform watersheds.
- Construct a region adjacency graph (RAG)
- Extract features for all edges in the graph
- Map the ground truth to the edges in the graph. (only for the training set)
for ds in ['train', 'test']:
rawDset = rawDsets[ds]
pmapDset = pmapDsets[ds]
gtDset = gtDsets[ds]
dataDset = computedData[ds]
# for each slice
for z in range(rawDset.shape[0]):
data = dataDset[z]
# get raw and pmap slice
raw = rawDset[z, ... ]
pmap = pmapDset[z, ... ]
# oversementation
overseg = nifty.segmentation.distanceTransformWatersheds(pmap, threshold=0.3)
overseg -= 1
data['overseg'] = overseg
# region adjacency graph
rag = nifty.graph.rag.gridRag(overseg)
data['rag'] = rag
# compute features
features = computeFeatures(raw=raw, pmap=pmap, rag=rag)
data['features'] = features
# map the gt to edge
if ds == 'train':
# the gt is on membrane level
# 0 at membranes pixels
# 1 at non-membrane pixels
gtImage = gtDset[z, ...]
# local maxima seeds
seeds = nifty.segmentation.localMaximaSeeds(gtImage)
# growing map
growMap = nifty.filters.gaussianSmoothing(1.0-gtImage, 1.0)
growMap += 0.1*nifty.filters.gaussianSmoothing(1.0-gtImage, 6.0)
gt = nifty.segmentation.seededWatersheds(growMap, seeds=seeds)
# map the gt to the edges
overlap = nifty.ground_truth.overlap(segmentation=overseg,
groundTruth=gt)
# edge gt
edgeGt = overlap.differentOverlaps(rag.uvIds())
data['edgeGt'] = edgeGt
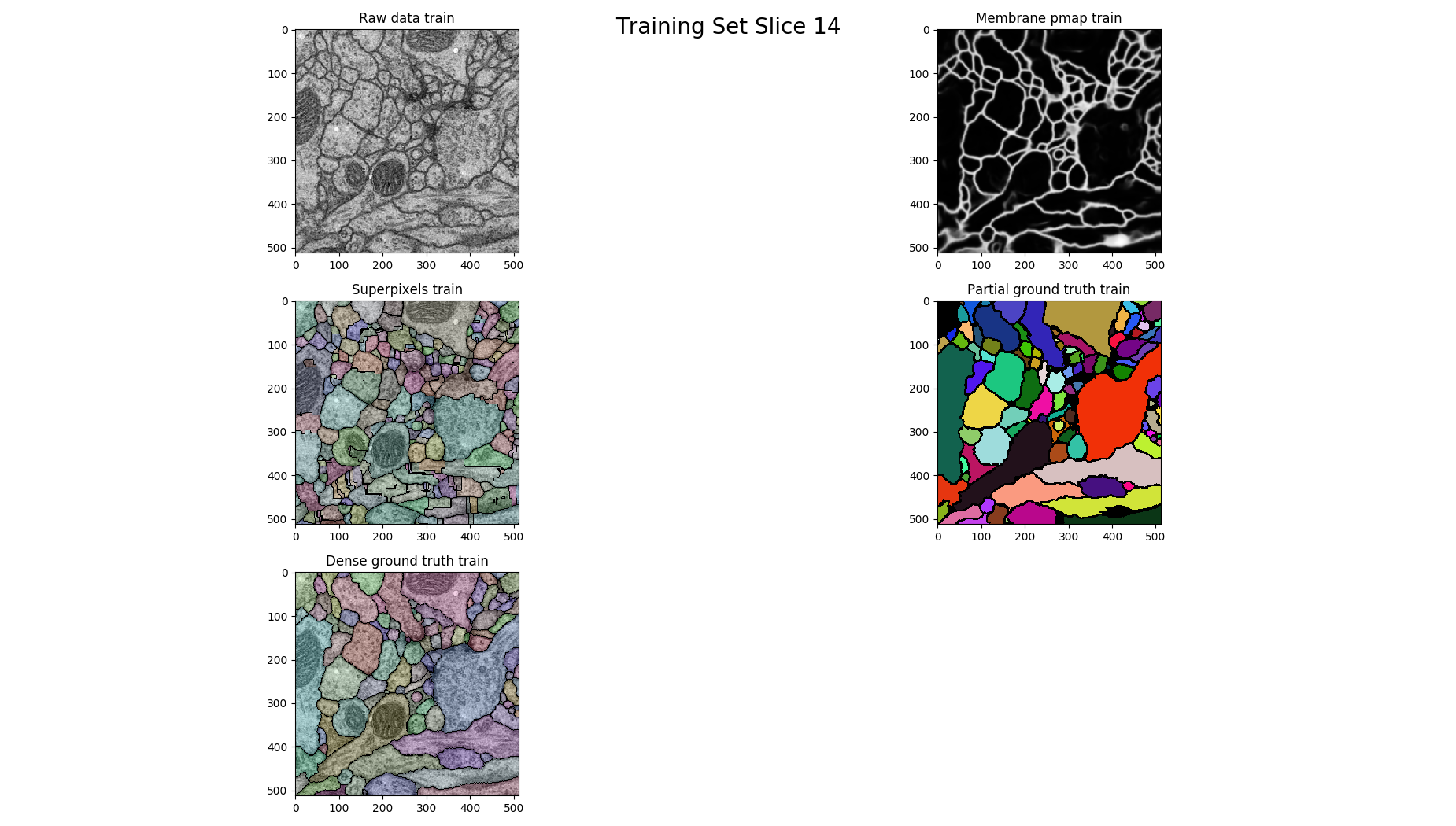
# plot each 14th
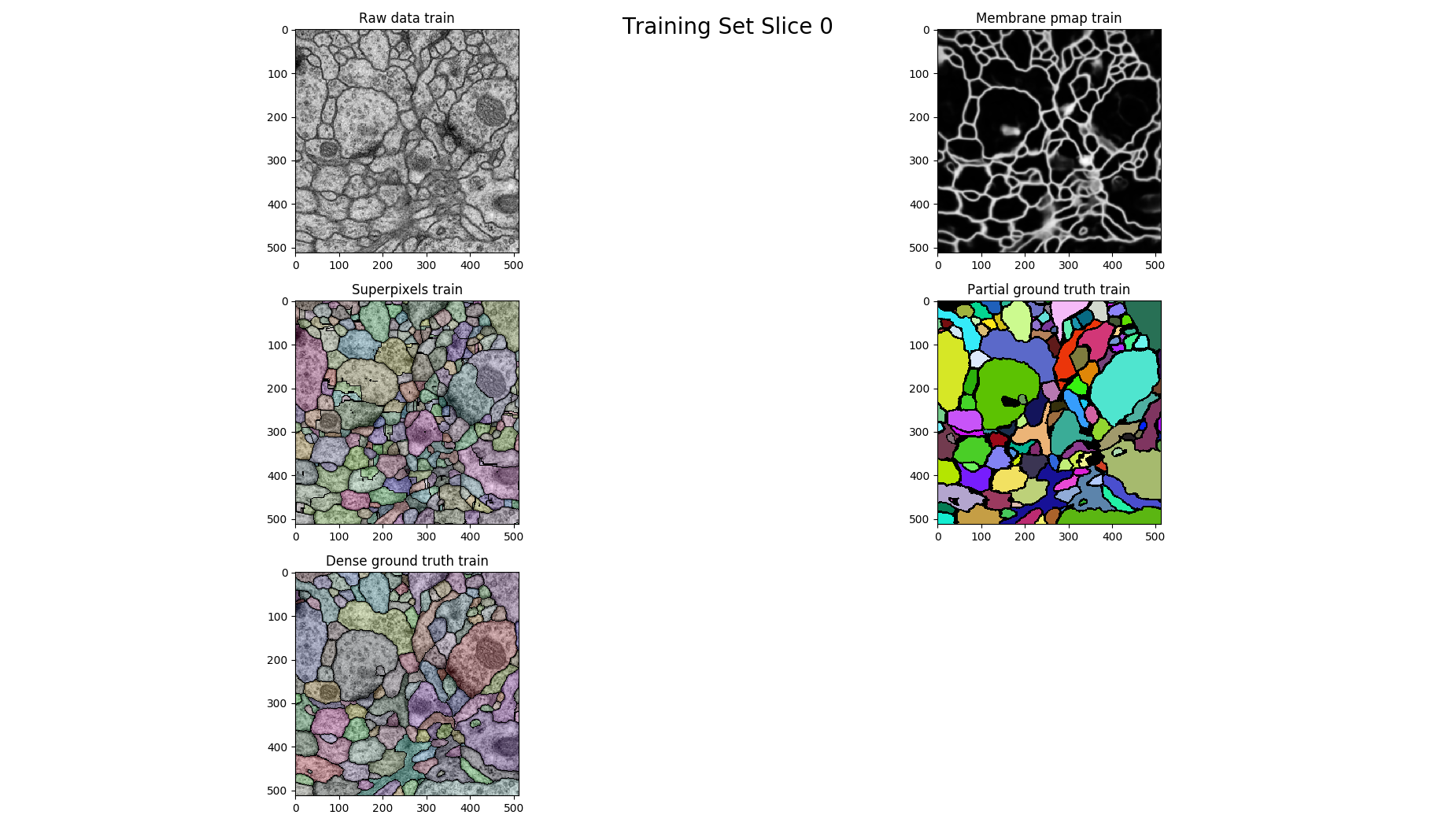
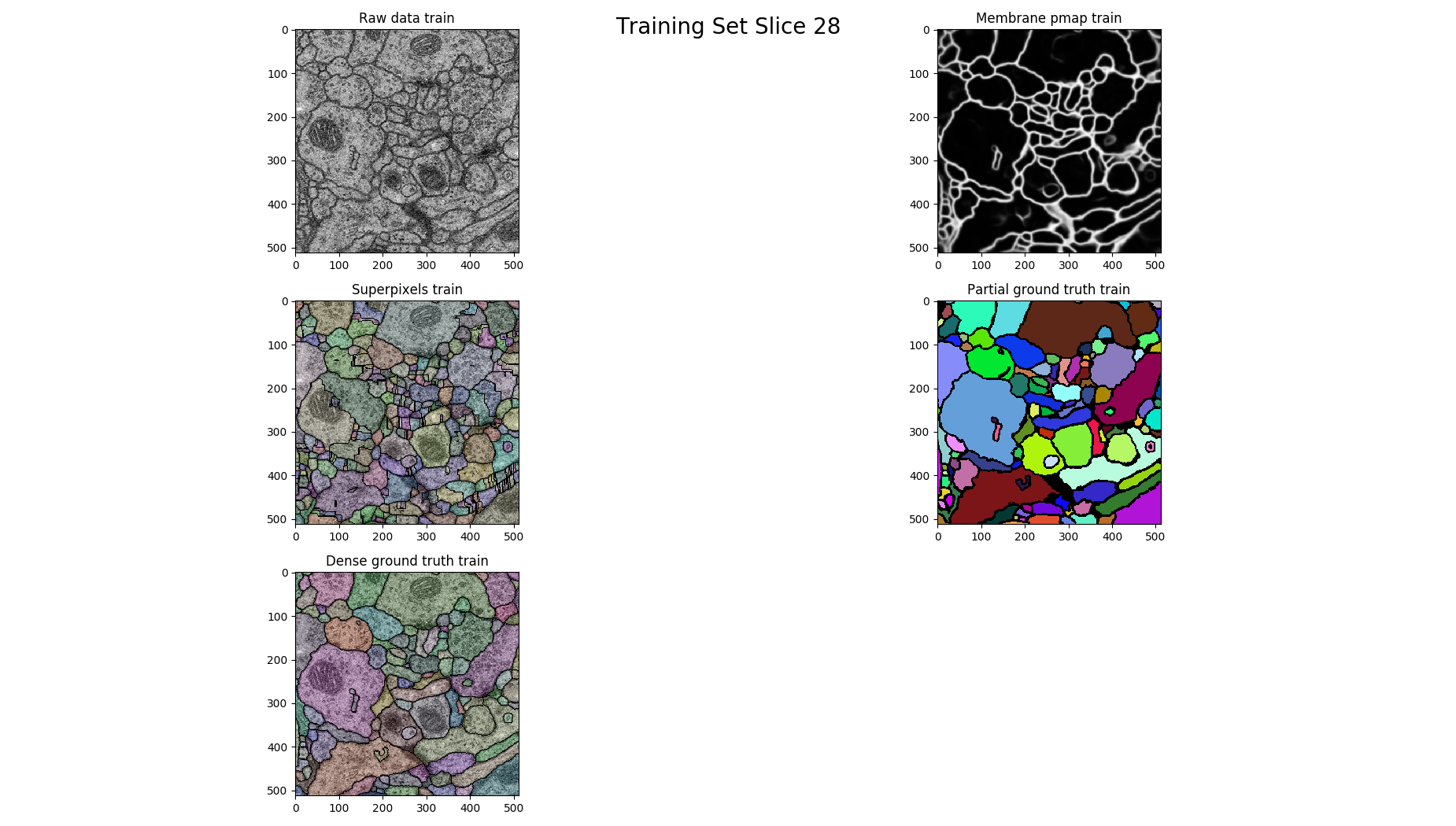
if z % 14 == 0 :
figure = pylab.figure()
figure.suptitle('Training Set Slice %d'%z, fontsize=20)
#fig = matplotlib.pyplot.gcf()
figure.set_size_inches(18.5, 10.5)
figure.add_subplot(3, 2, 1)
pylab.imshow(raw, cmap='gray')
pylab.title("Raw data %s"%(ds))
figure.add_subplot(3, 2, 2)
pylab.imshow(pmap, cmap='gray')
pylab.title("Membrane pmap %s"%(ds))
figure.add_subplot(3, 2, 3)
pylab.imshow(nifty.segmentation.segmentOverlay(raw, overseg, 0.2, thin=False))
pylab.title("Superpixels %s"%(ds))
figure.add_subplot(3, 2, 4)
pylab.imshow(seeds, cmap=nifty.segmentation.randomColormap(zeroToZero=True))
pylab.title("Partial ground truth %s" %(ds))
figure.add_subplot(3, 2, 5)
pylab.imshow(nifty.segmentation.segmentOverlay(raw, gt, 0.2, thin=False))
pylab.title("Dense ground truth %s" %(ds))
pylab.tight_layout()
pylab.show()
else:
data['edgeGt'] = None
Build the training set:¶
We only use high confidence boundaries.
dataDset = computedData[ds]
trainingSet = {'features':[],'labels':[]}
for ds in ['train']:
rawDset = rawDsets[ds]
pmapDset = pmapDsets[ds]
gtDset = gtDsets[ds]
dataDset = computedData[ds]
# for each slice
for z in range(rawDset.shape[0]):
data = dataDset[z]
rag = data['rag']
edgeGt = data['edgeGt']
features = data['features']
# we use only edges which have
# a high certainty
where1 = numpy.where(edgeGt > 0.85)[0]
where0 = numpy.where(edgeGt < 0.15)[0]
trainingSet['features'].append(features[where0,:])
trainingSet['features'].append(features[where1,:])
trainingSet['labels'].append(numpy.zeros(len(where0)))
trainingSet['labels'].append(numpy.ones(len(where1)))
features = numpy.concatenate(trainingSet['features'], axis=0)
labels = numpy.concatenate(trainingSet['labels'], axis=0)
Train the random forest (RF):¶
rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=200, oob_score=True)
rf.fit(features, labels)
print("OOB SCORE",rf.oob_score_)
Out:
OOB SCORE 0.981860916662
Predict Edge Probabilities & Optimize Multicut Objective:¶
Predict the edge probabilities with the learned random forest classifier. Set up a multicut objective and find the argmin with an ILP solver (if available).
for ds in ['test']:
rawDset = rawDsets[ds]
pmapDset = pmapDsets[ds]
gtDset = gtDsets[ds]
dataDset = computedData[ds]
# for each slice
for z in range(rawDset.shape[0]):
data = dataDset[z]
raw = rawDset[z,...]
pmap = pmapDset[z,...]
overseg = data['overseg']
rag = data['rag']
edgeGt = data['edgeGt']
features = data['features']
predictions = rf.predict_proba(features)[:,1]
# setup multicut objective
MulticutObjective = rag.MulticutObjective
eps = 0.00001
p1 = numpy.clip(predictions, eps, 1.0 - eps)
weights = numpy.log((1.0-p1)/p1)
objective = MulticutObjective(rag, weights)
# do multicut obtimization
if nifty.Configuration.WITH_CPLEX:
solver = MulticutObjective.multicutIlpCplexFactory().create(objective)
elif nifty.Configuration.WITH_GUROBI:
solver = MulticutObjective.multicutIlpGurobiFactory().create(objective)
else:
solver = MulticutObjective.ccFusionMoveBasedFactory().create(objective)
arg = solver.optimize(visitor=MulticutObjective.verboseVisitor())
result = nifty.graph.rag.projectScalarNodeDataToPixels(rag, arg)
# plot for each 14th slice
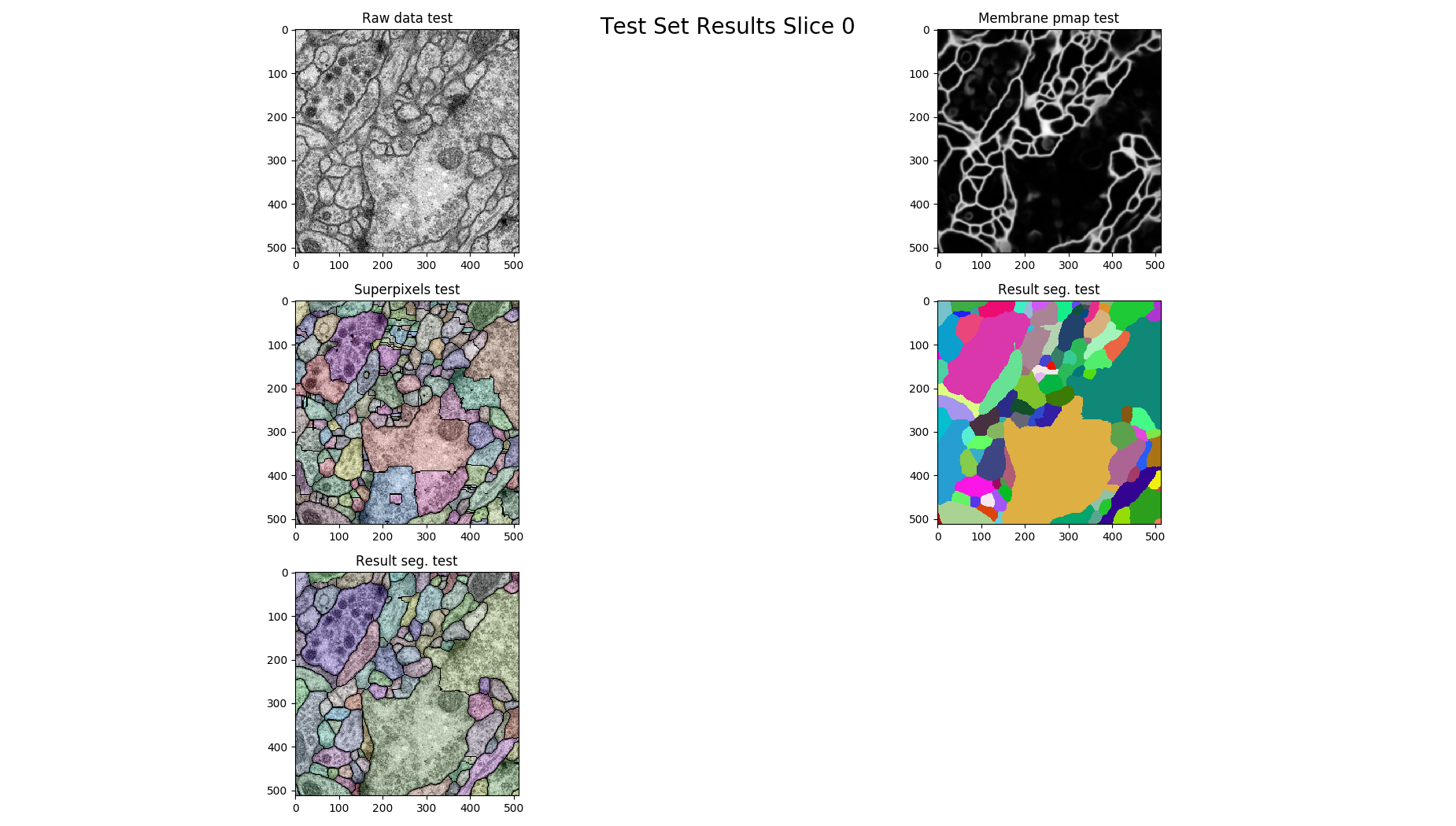
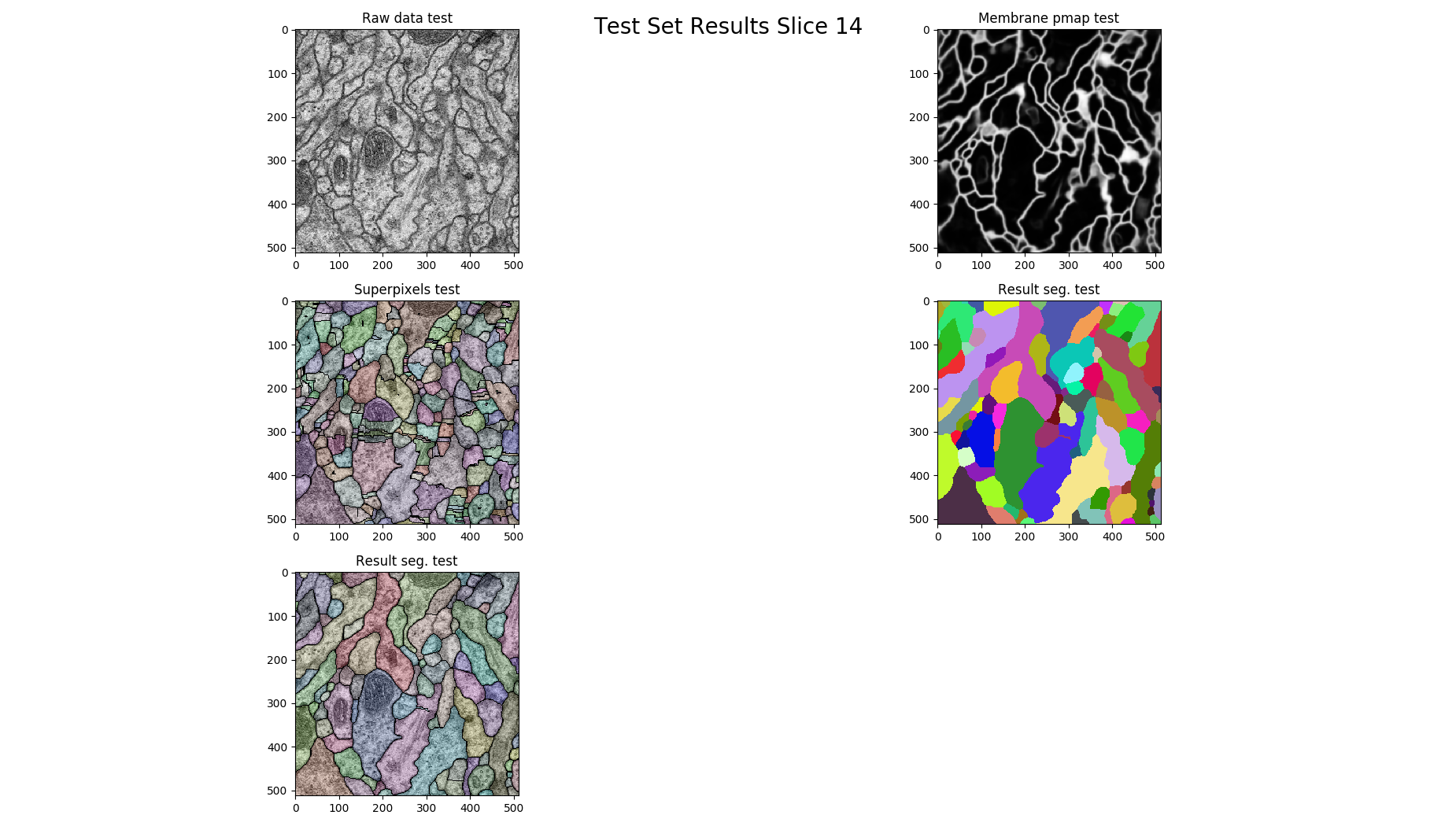
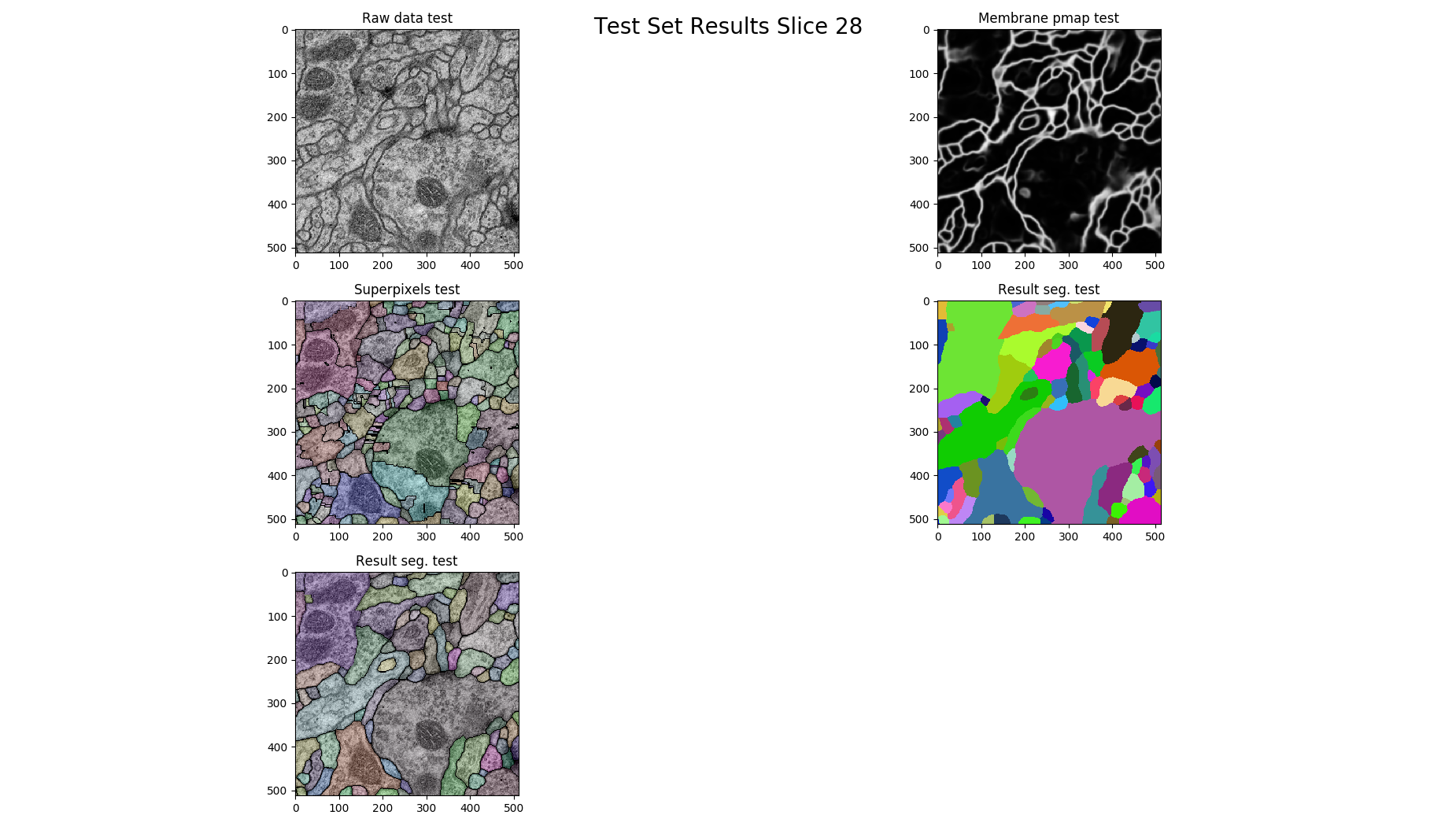
if z % 14 == 0:
figure = pylab.figure()
figure.suptitle('Test Set Results Slice %d'%z, fontsize=20)
#fig = matplotlib.pyplot.gcf()
figure.set_size_inches(18.5, 10.5)
figure.add_subplot(3, 2, 1)
pylab.imshow(raw, cmap='gray')
pylab.title("Raw data %s"%(ds))
figure.add_subplot(3, 2, 2)
pylab.imshow(pmap, cmap='gray')
pylab.title("Membrane pmap %s"%(ds))
figure.add_subplot(3, 2, 3)
pylab.imshow(nifty.segmentation.segmentOverlay(raw, overseg, 0.2, thin=False))
pylab.title("Superpixels %s"%(ds))
figure.add_subplot(3, 2, 4)
pylab.imshow(result, cmap=nifty.segmentation.randomColormap())
pylab.title("Result seg. %s" %(ds))
figure.add_subplot(3, 2, 5)
pylab.imshow(nifty.segmentation.segmentOverlay(raw, result, 0.2, thin=False))
pylab.title("Result seg. %s" %(ds))
pylab.tight_layout()
pylab.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 2 minutes 15.624 seconds)